Smart Technology
Temperature Indicating Coatings, Pigments, Ink, Paint & Labels Photochromic Paint, Ink Dyes, Powder, Slurry and Masterbatch
-

Irreversible Inks
Permanent change thermochromic ink is a high temperature activated, permanent change ink.
-

Thermochromic Masterbatch
Temperature sensitive thermochromic pellets containing Leuco Dyes which change from colored to colorless as temperature rises.
-

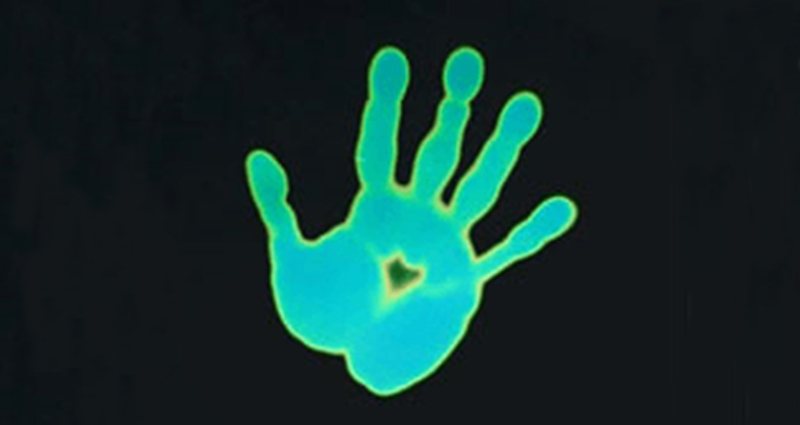
Thermochromic
Thermochromics, like liquid crystals and leuco dyes, predominantly change color in response to temperature fluctuations.
-

Photochromic
Unique, high precision temperature sensitive phase change indicators with color change effects.
-

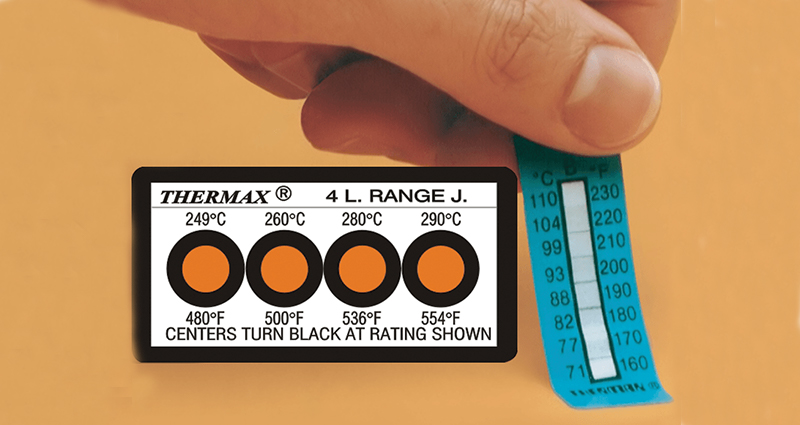
Irreversible Temperature Labels
Photochromics (PCs) transform from clear to color by changing their chemical structure after absorbing UV light.
-

Wax Melts
When the rated temperature is exceeded, the chemical melts and is absorbed by the substrate, causing a permanent color change to black.
-

Microencapsulation
The most versatile and successful way of stabilizing, packaging, and protecting liquid crystal and leuco dye products.
-

Thermochromics Leuco Dye
Changes color with changes in temperature.
-

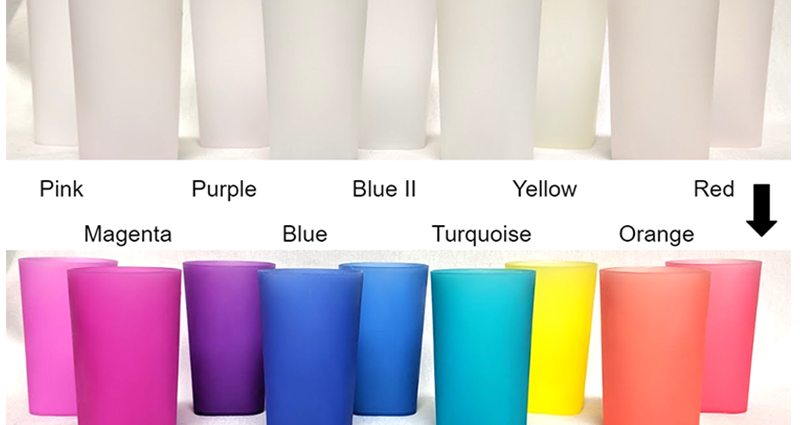
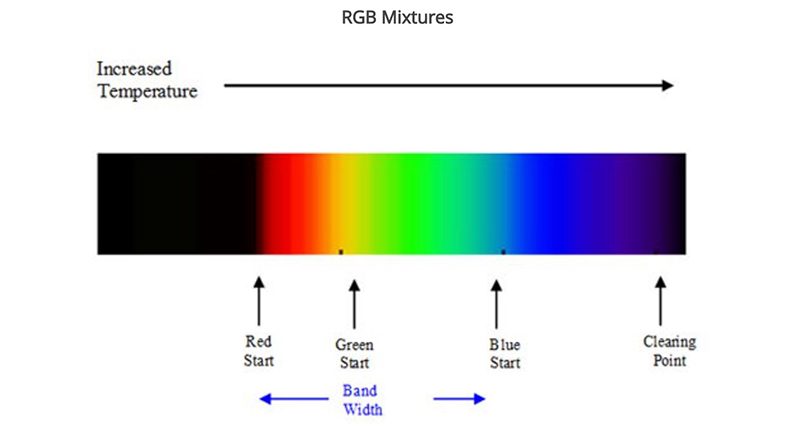
LIQUID CRYSTAL THERMOMETERS
Optically active mixtures of organic chemicals that can be highly temperature sensitive and change to many colors.
-

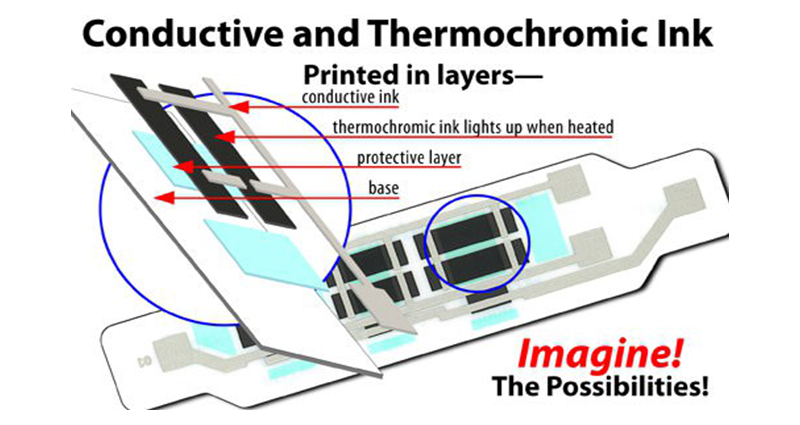
Conductive and Thermochromic Ink
Customized solutions to create various battery powered color changing designs, displays, and messages.
-

Resources For Thermographic Liquid Crystal or TLC Products
Resources for the liquid crystal and TLC products
-

Liquid Crystal Formulations
Highly temperature sensitive, change to many colors, and are more expensive than leuco dyes.
Read More About Smart Technology
Definitions
Temperature indicating coatings and materials include chemical indicators, labels, pigments, paints or other indicators that change color when exposed to a certain temperature. These products are either irreversible and designed for one-time use providing evidence of attained temperature or are reversible and can change back and forth to provide an indication of the current temperature. Photochromic pigments, paints and inks change color when exposed to UV light reversing to colorless when removed from the UV light exposure.
Operating Principle
Temperature indicating labels, coating, paint, ink and pigments incorporate materials that exhibit thermochromism, a physical property that undergoes a change in color in response to a change in temperature. Photochromic paints exhibit a photochemical reaction to UV light changing from an essentially colorless state to colored.
Microencapsulating Thermochromic Liquid Crystals and Leuco Dyes increases accuracy, stability and life expectancy of the product. Leuco Dyes, Thermochromic Liquid Crystals and Chemical Indicators are thermochromic substances LCR Hallcrest offers as a label, coating, pigment and paint. Photochromic Paint is also available as a Powder, Slurry, Ink and Masterbatch.
Categories
Coating – Coatings are a layer of something deposited upon a material surface to add or enhance desired properties.
Pigment – a dry insoluble color matter or substance usually pulverized which when suspended in a liquid vehicle becomes a paint, ink, etc.
Paint – is a pigmented liquid mixture used on a substrate as a decorative or protective coating. Color changing paint can be used to monitor surface temperature and alert operators to potential hazards, maintenance requirements, etc.
Ink – A colored liquid or powder that is printed, sprayed, rolled to substrates to create markings, patterns or graphics. Color changing inks are smart and react to environmental fluctuations with color change.
Labels – an adhesive backed thin film for adhering to a surface with color changing material that can be either a reversible or a permanent change indicator with a scale or alert color.
Read Less